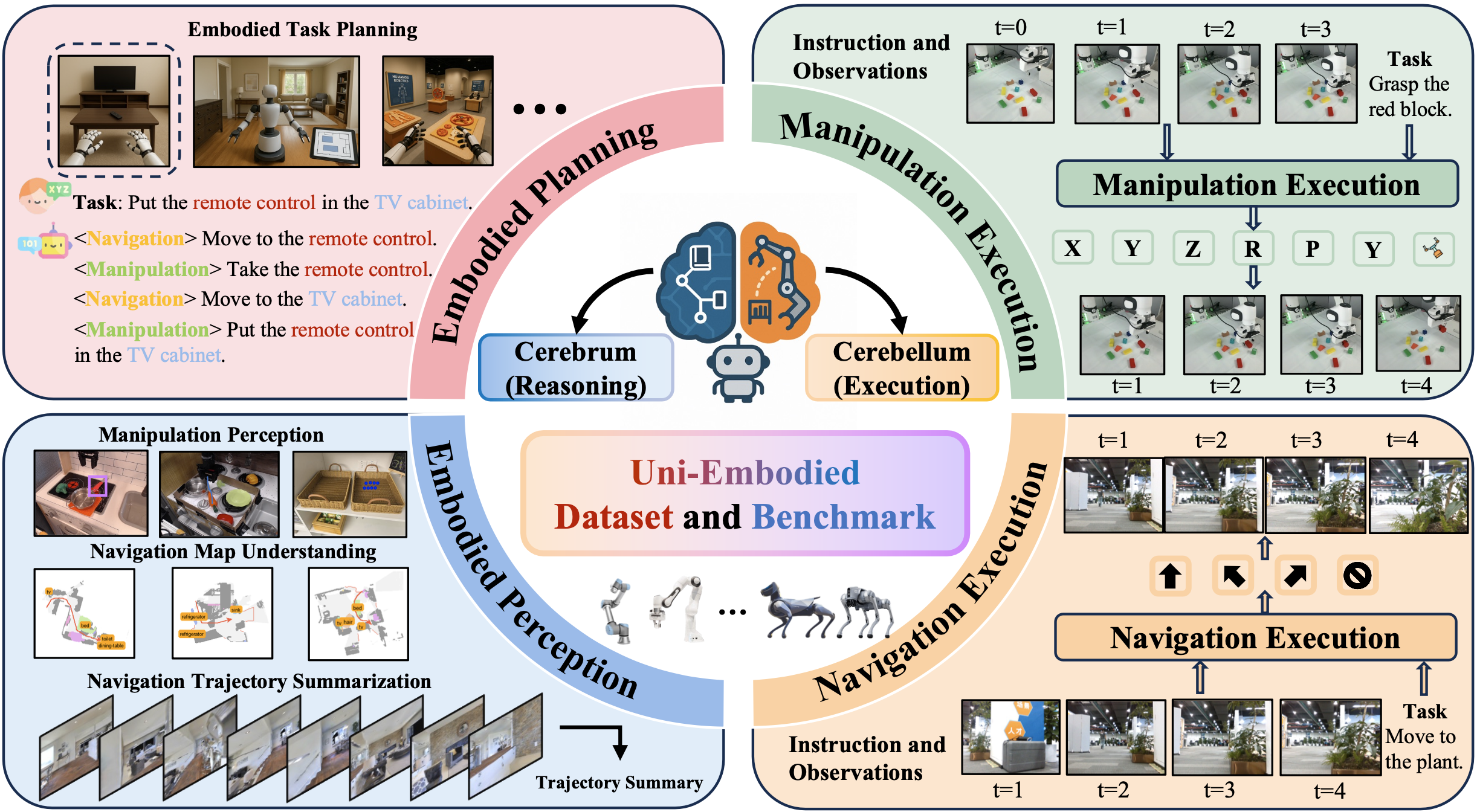
Embodied intelligence is a core challenge in the pursuit of artificial general intelligence (AGI), requiring the seamless integration of planning, perception, and execution to enable agents to perform physical tasks effectively. While recent vision-language models (VLMs) have shown strong performance in isolated capabilities, their ability to jointly exhibit all three embodied skills remains unclear, impeding the development of unified embodied systems.
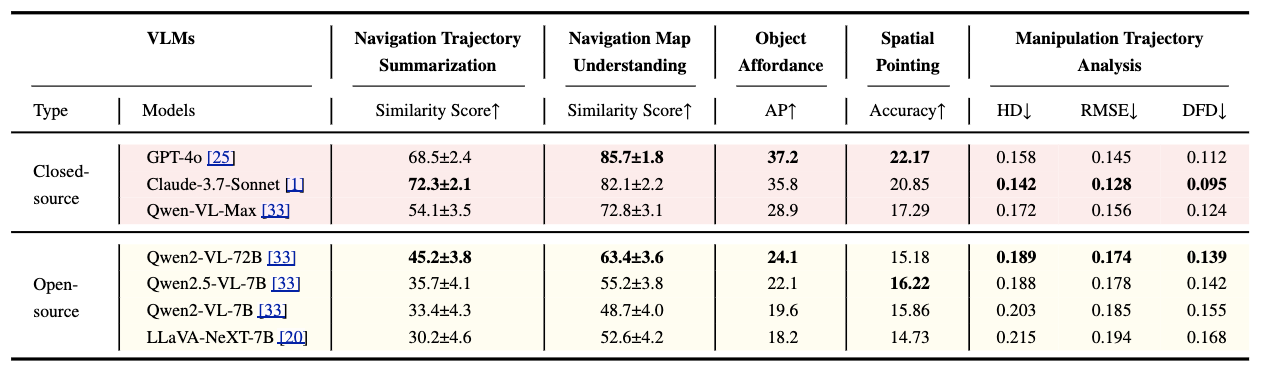
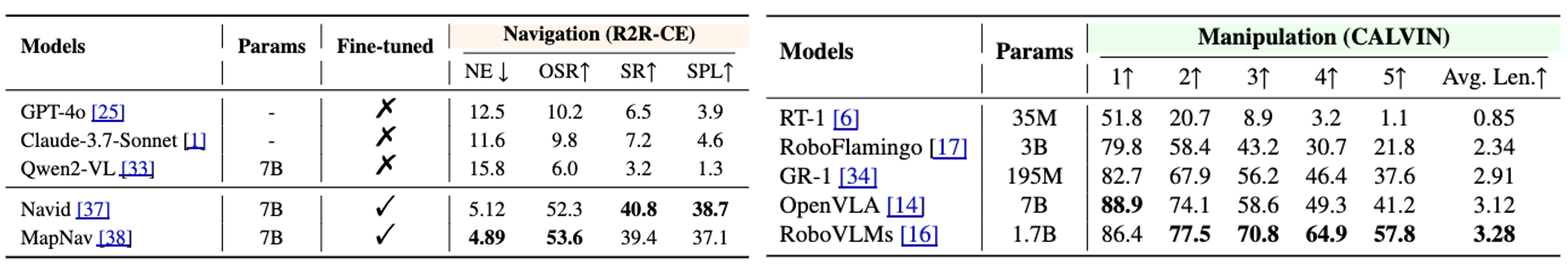
In this paper, we propose Uni-Embodied, the first comprehensive benchmark designed to evaluate VLMs across the three key dimensions of embodied intelligence: planning, perception, and execution. Our benchmark includes nine diverse tasks—ranging from complex and simple embodied planning to trajectory summarization, map understanding, affordance recognition, spatial pointing, manipulation analysis, and execution in both navigation and manipulation contexts.
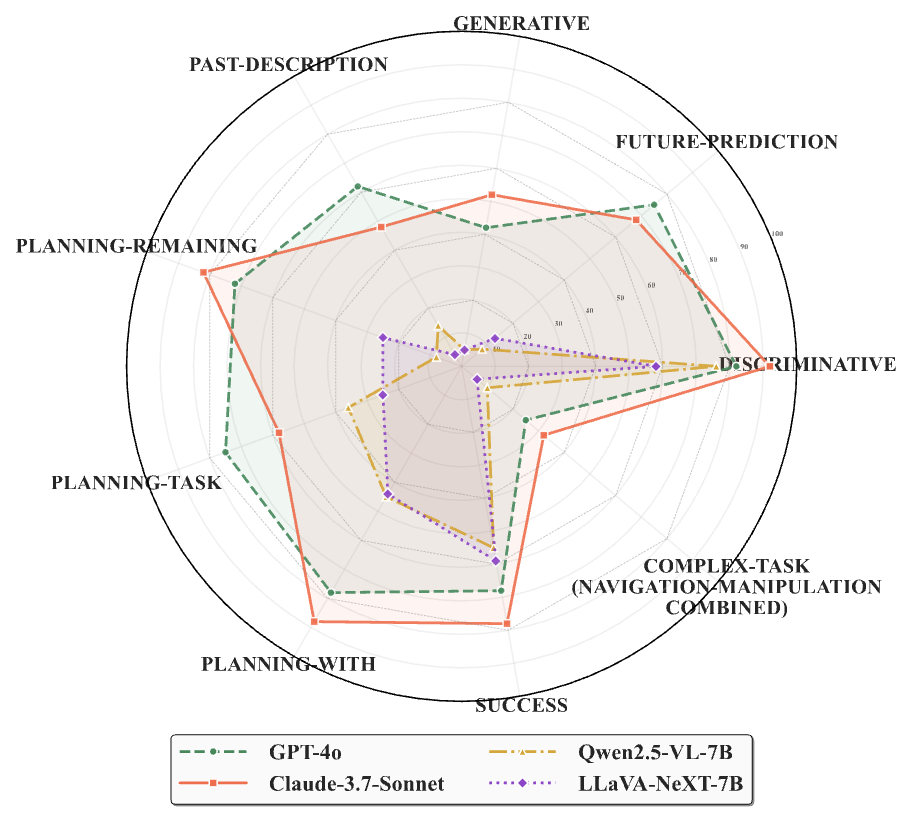
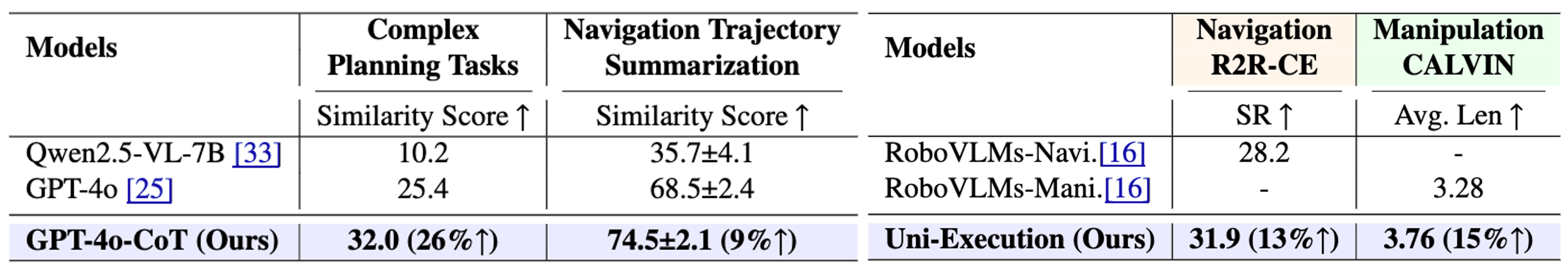
Extensive experiments on leading open-source and closed-source VLMs demonstrate that current models struggle to achieve balanced performance across all three dimensions. Notably, we observe that enhancing planning and perception often compromises execution, while focusing on execution significantly degrades planning and perception capabilities—revealing fundamental limitations in existing approaches.
We further explore strategies such as chain-of-thought prompting and hybrid training to selectively improve specific embodied capabilities. These findings offer valuable insights for the development of more robust and unified embodied intelligence systems, critical for advancing real-world robotic applications.